Connecting via Cmdline (Mac / Linux)
TLDR - Quick Summary
What: Connect to SFTP Gateway via Mac/Linux terminal (no extra software needed)
SSH Key:
chmod 400 key.pem && sftp -i key.pem user@ipPassword:
sftp user@ipthen enter password when promptedCommands:
putto upload,getto download,lsto list,exitto quit
Overview
Using sftp from terminal isn't as popular as GUI-based SFTP clients,
however it does not require the installation of extra software.
Note: connecting via terminal only works for Mac or Linux, as Windows does not have a built-in sftp command.
In order to sftp via terminal, you will need:
- The public IP address of the server.
- The username you will log in as.
- An SSH private key or the password associated with the username.
Open a new terminal window and follow the instructions below.
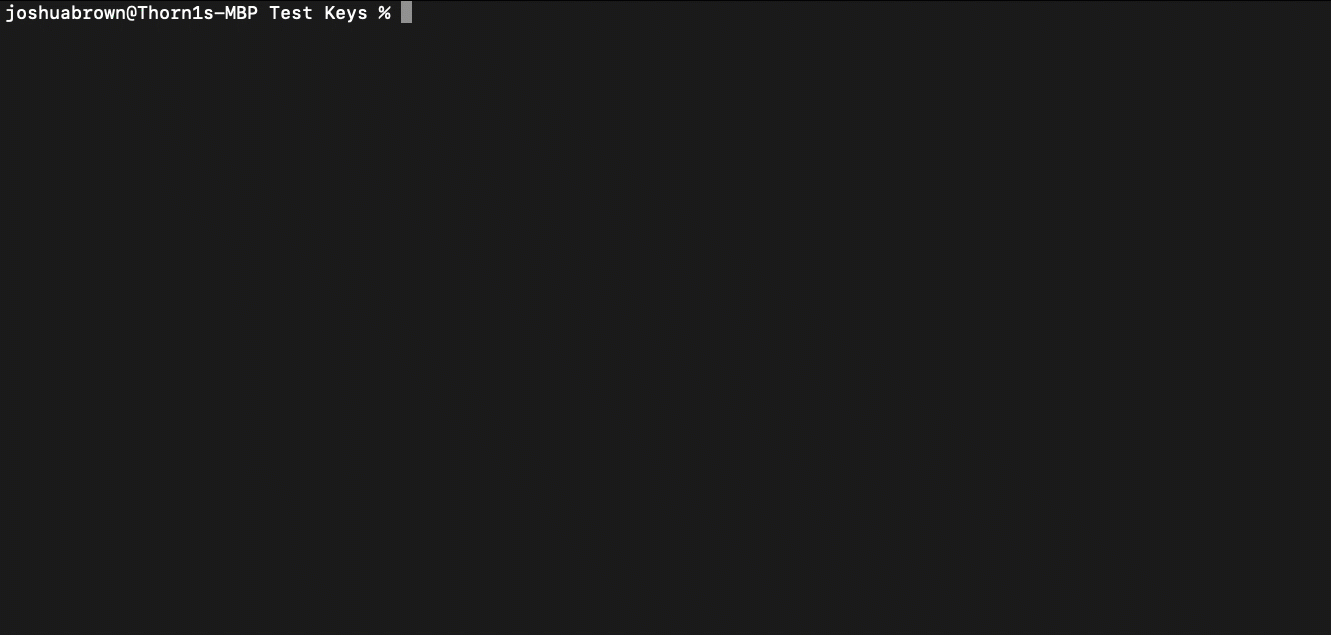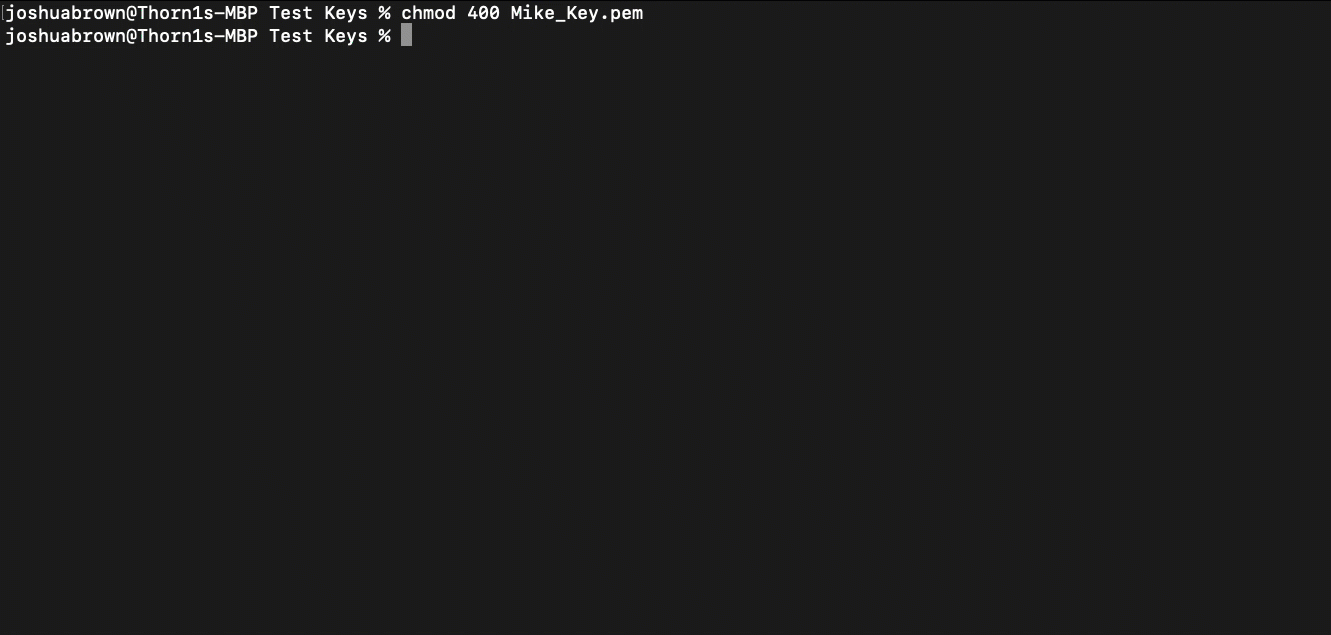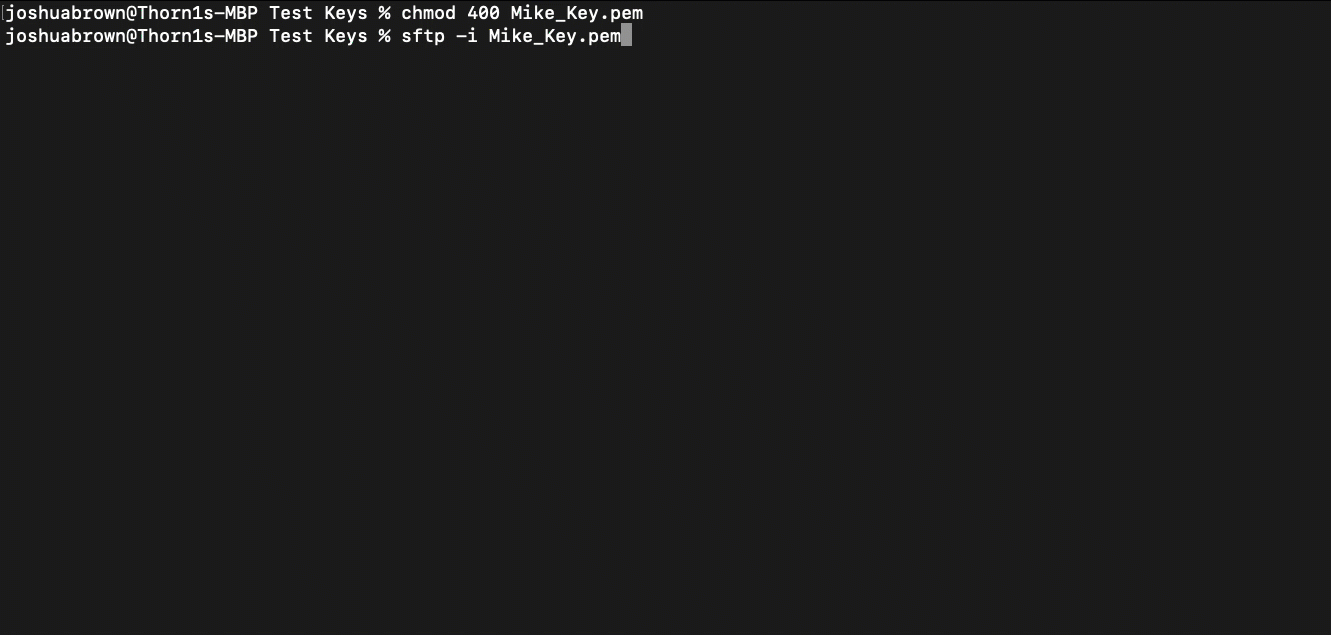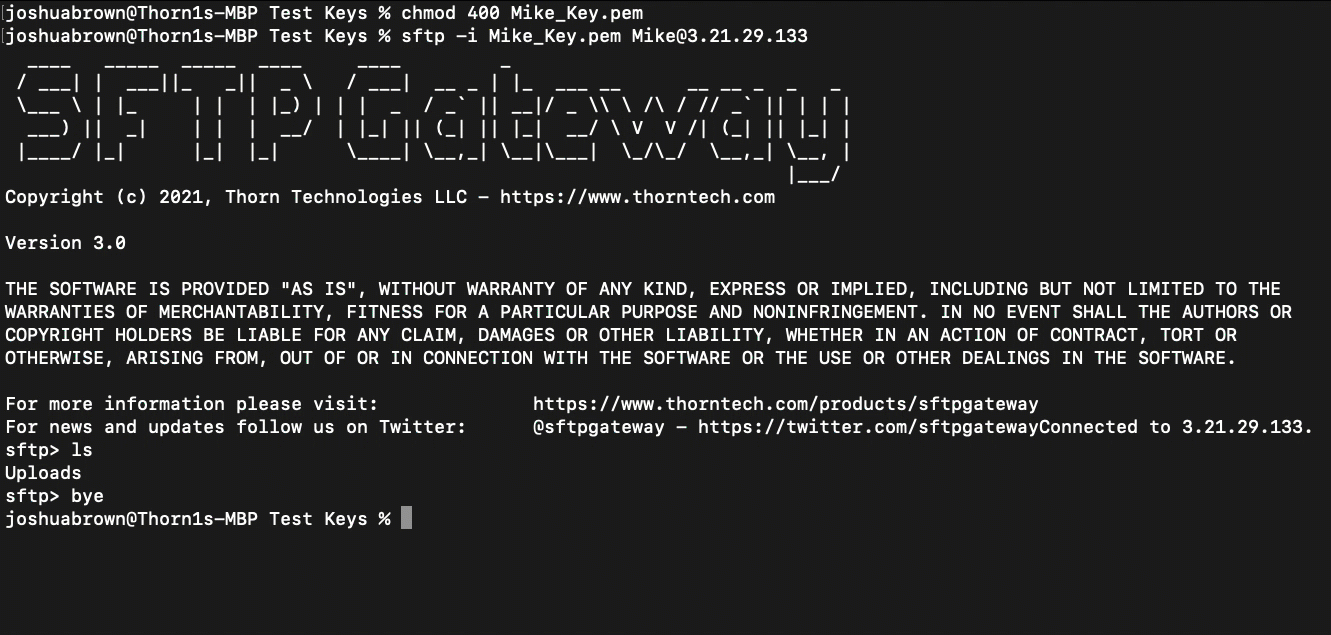
SSH Key Login
In order to use your private key at the command line, you need to tighten permissions. Run the following command:
chmod 400 <private key file>
(This only needs to be done once)
Log into the SFTP Gateway server by running:
sftp -i <private key file> <username>@<public ip>
You may encounter a warning like this:
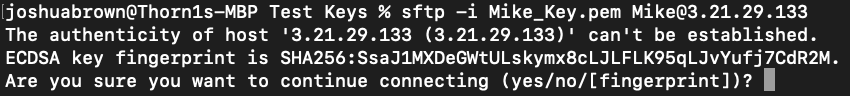
Type yes and hit enter.
If your SSH key is passphrase protected, you should see something like:

Enter your passphrase to continue.
If successful, you should see a new prompt that says:
Connected to <public ip>.
sftp>
GIF Demonstration
Password Login
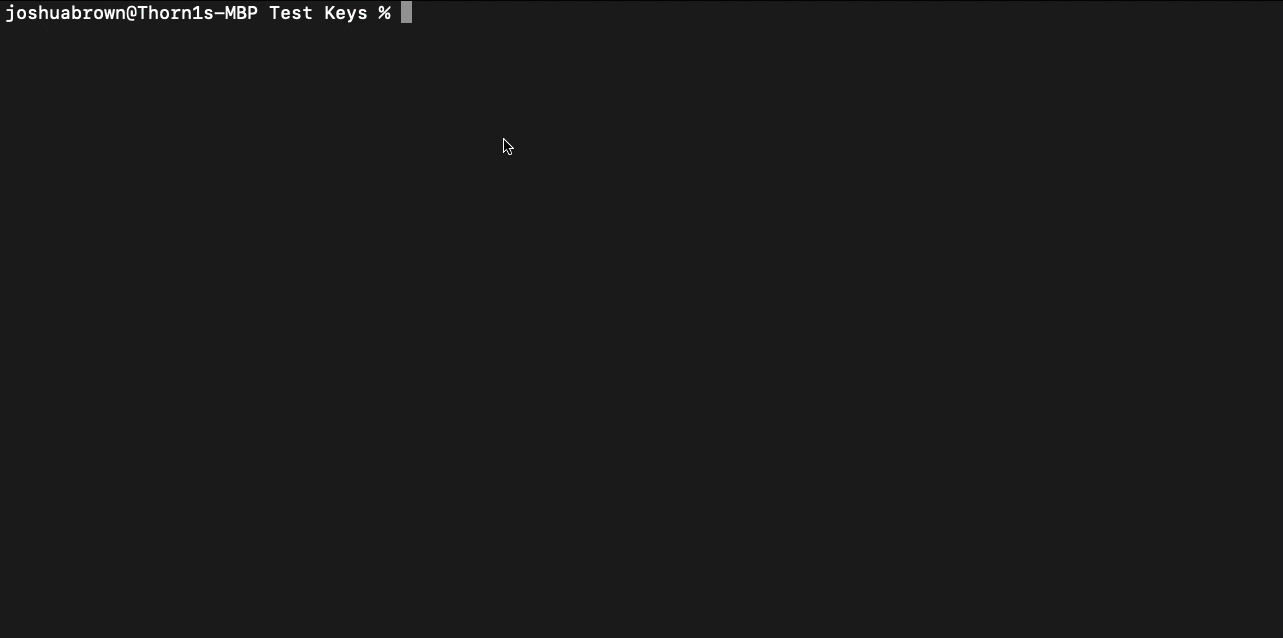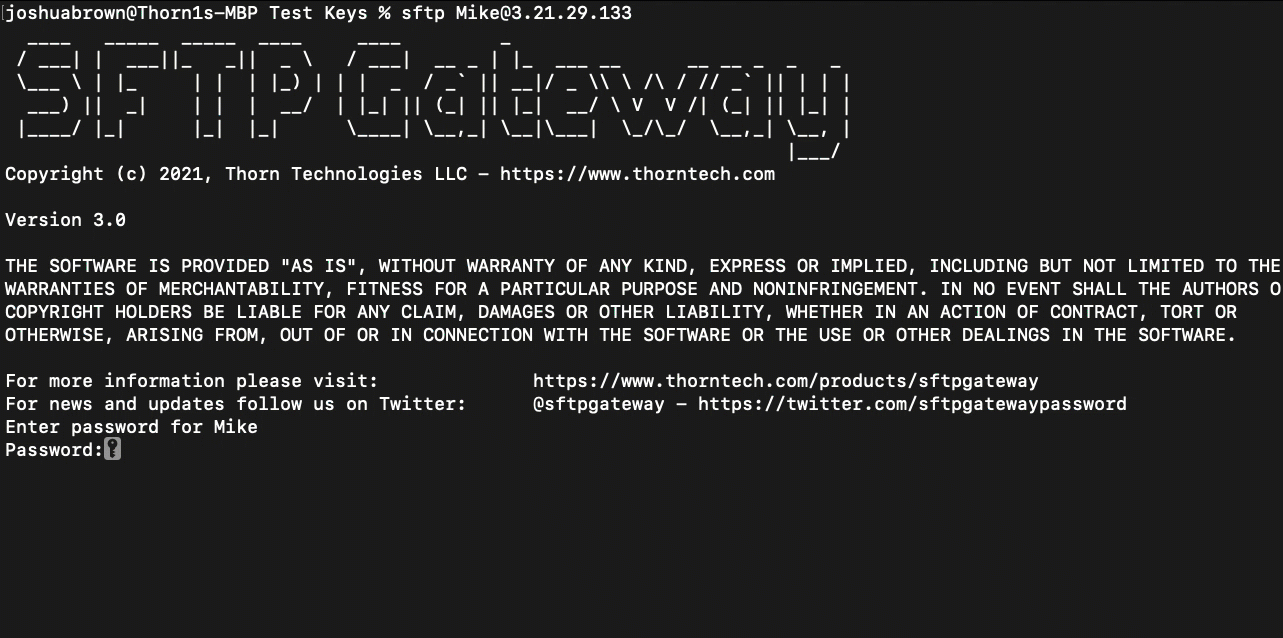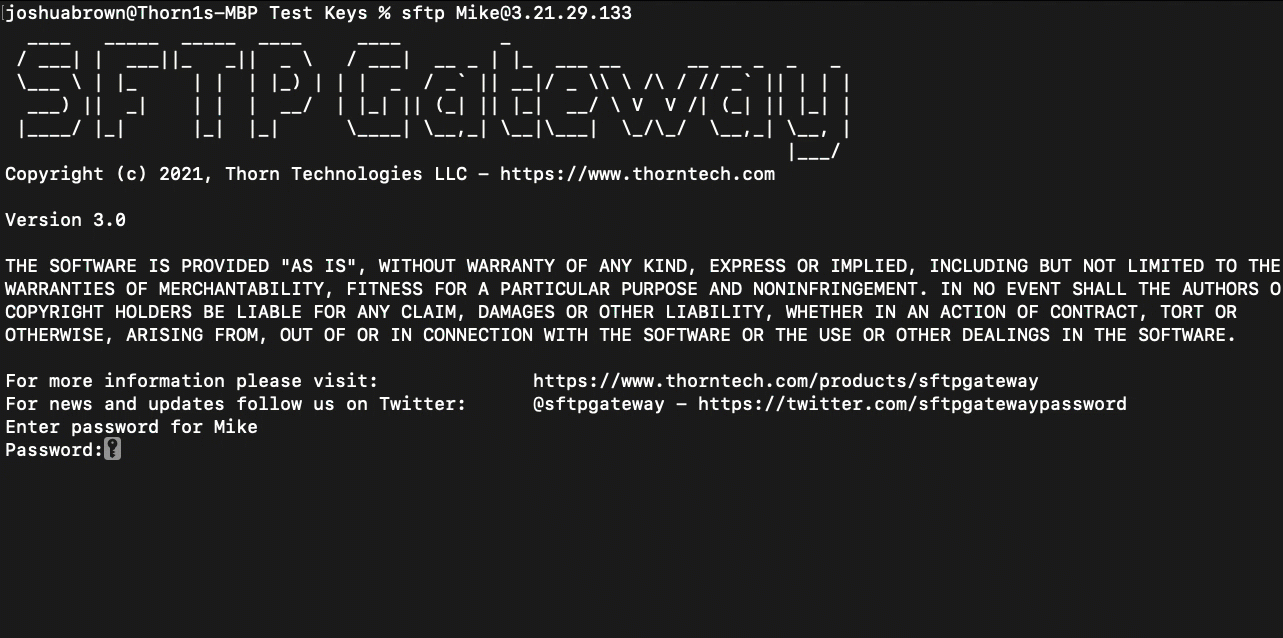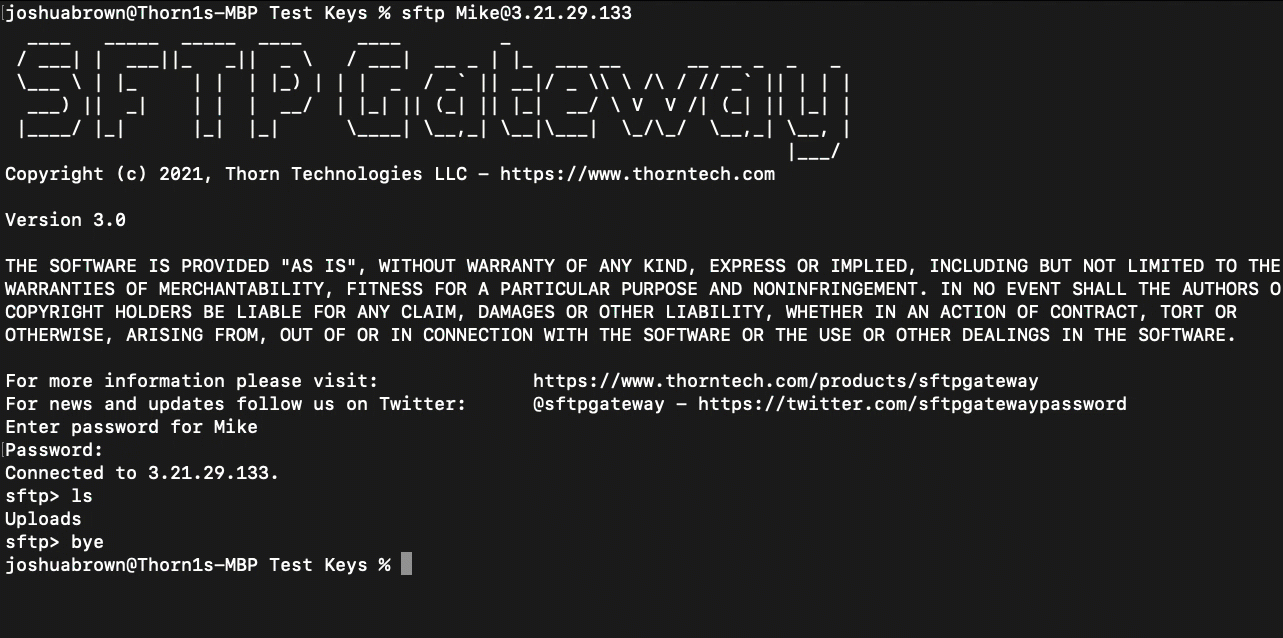
In order to connect to the server with a password, run the following command:
sftp <username>@<public ip>
You may encounter a warning like this:

Type yes and hit enter.
The terminal should then prompt you for a password, like so:
Enter password for <username>
Password:
Enter your password and hit enter.
If successful, you should see a new prompt that says:
Connected to <public ip>.
sftp>
To end your SFTP session, either run exit or press [control + d].
GIF Demonstration
Available Commands
Once connected to the server, you will be able to run SFTP commands:
bye Quit sftp
cd path Change remote directory to 'path'
chgrp [-h] grp path Change group of file 'path' to 'grp'
chmod [-h] mode path Change permissions of file 'path' to 'mode'
chown [-h] own path Change owner of file 'path' to 'own'
df [-hi] [path] Display statistics for current directory or
filesystem containing 'path'
exit Quit sftp
get [-afpR] remote [local] Download file
help Display this help text
lcd path Change local directory to 'path'
lls [ls-options [path]] Display local directory listing
lmkdir path Create local directory
ln [-s] oldpath newpath Link remote file (-s for symlink)
lpwd Print local working directory
ls [-1afhlnrSt] [path] Display remote directory listing
lumask umask Set local umask to 'umask'
mkdir path Create remote directory
progress Toggle display of progress meter
put [-afpR] local [remote] Upload file
pwd Display remote working directory
quit Quit sftp
reget [-fpR] remote [local] Resume download file
rename oldpath newpath Rename remote file
reput [-fpR] local [remote] Resume upload file
rm path Delete remote file
rmdir path Remove remote directory
symlink oldpath newpath Symlink remote file
version Show SFTP version
!command Execute 'command' in local shell
! Escape to local shell
? Synonym for help
Example:
